Articles
-
 This is an article about doing proposals The Wrong Way. That is what you have to do when you are required to submit a proposal your company is not prepared for and you don’t have the information you need to win it. With all the problems and weaknesses that you have to overcome, maybe your company shouldn’t be bidding it at all, but that decision isn’t up to you. The best practices are all about preparation and won’t help you in adverse circumstances like these. So you’ve got some challenges
This is an article about doing proposals The Wrong Way. That is what you have to do when you are required to submit a proposal your company is not prepared for and you don’t have the information you need to win it. With all the problems and weaknesses that you have to overcome, maybe your company shouldn’t be bidding it at all, but that decision isn’t up to you. The best practices are all about preparation and won’t help you in adverse circumstances like these. So you’ve got some challenges- 0 comments
- 13,790 views
-
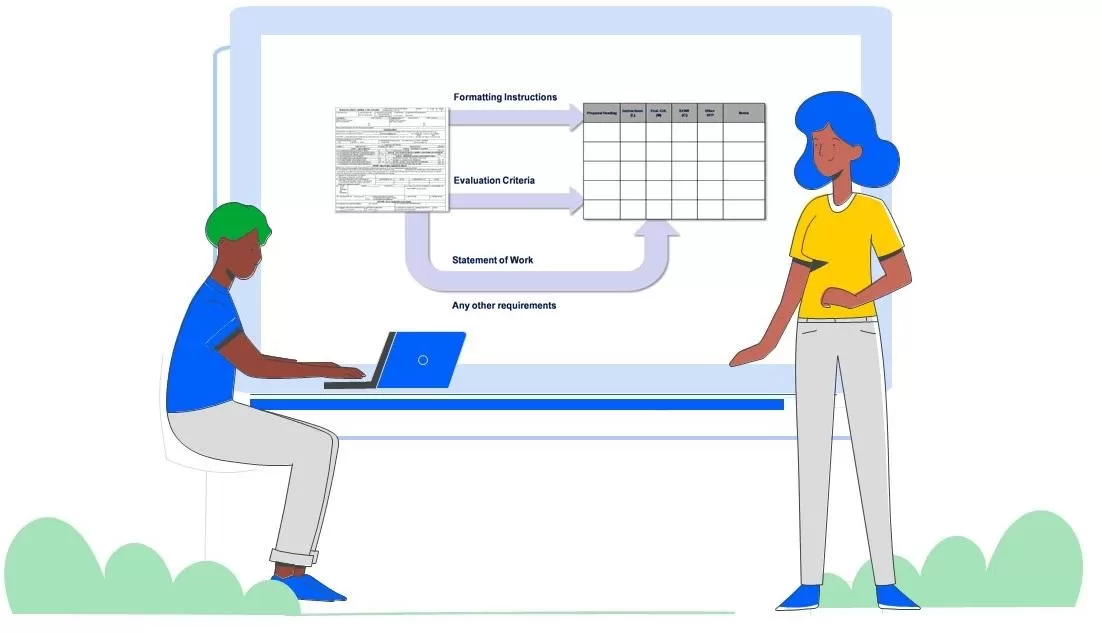 The process detailed below for creating a proposal compliance matrix, shows writers where in the proposal they should address every RFP requirement: Definition: A proposal compliance matrix uses a grid to show which RFP requirements are relevant to each section of the proposal. A proposal compliance matrix shows proposal writers where the customer expects to find each require addressed in the proposal. A proposal compliance matrix shows exactly which RFP r
The process detailed below for creating a proposal compliance matrix, shows writers where in the proposal they should address every RFP requirement: Definition: A proposal compliance matrix uses a grid to show which RFP requirements are relevant to each section of the proposal. A proposal compliance matrix shows proposal writers where the customer expects to find each require addressed in the proposal. A proposal compliance matrix shows exactly which RFP r- 0 comments
- 30,325 views
-
 A lot of improvisation usually goes into proposal efforts. Proposal management is often an assignment to figure out how to do something while doing it. This can result in conflicts in expectations. Conflicts like these are best resolved before they manifest. Plus it’s good not to set yourself up for failure by going in with the wrong expectations. The list below is written from the proposal manager’s point of view. And it applies to consultants as well as employees. But you can also use it
A lot of improvisation usually goes into proposal efforts. Proposal management is often an assignment to figure out how to do something while doing it. This can result in conflicts in expectations. Conflicts like these are best resolved before they manifest. Plus it’s good not to set yourself up for failure by going in with the wrong expectations. The list below is written from the proposal manager’s point of view. And it applies to consultants as well as employees. But you can also use it- 0 comments
- 13,287 views
-
 Warning: This article challenges things people may have learned about proposals when they got started. It's good to learn better ways of doing things. But I find it amazing how much resistance there is to change in this area and how much it holds improving proposal quality back. So forgive me if I'm a little too honest... With the thousands of subscribers and hundreds of companies I’ve worked with, I’ve never seen one use the color team model to achieve consistently effective proposal revie
Warning: This article challenges things people may have learned about proposals when they got started. It's good to learn better ways of doing things. But I find it amazing how much resistance there is to change in this area and how much it holds improving proposal quality back. So forgive me if I'm a little too honest... With the thousands of subscribers and hundreds of companies I’ve worked with, I’ve never seen one use the color team model to achieve consistently effective proposal revie- 0 comments
- 14,108 views
-
 Who do you need on your proposal team? The place to start is with what activities need to be covered and what skills are needed. The easiest way to account for all the activities and corresponding skill requirements is to categorize them by the roles that people play in proposal development. Proposal development roles We prefer to define roles functionally. It doesn’t matter how many people you have doing the work, as long as you have every function covered. On a small proposal you migh
Who do you need on your proposal team? The place to start is with what activities need to be covered and what skills are needed. The easiest way to account for all the activities and corresponding skill requirements is to categorize them by the roles that people play in proposal development. Proposal development roles We prefer to define roles functionally. It doesn’t matter how many people you have doing the work, as long as you have every function covered. On a small proposal you migh- 0 comments
- 13,072 views
-
 Joining a company should be about opportunity. Personal, professional, and fiscal. But where does that opportunity come from? Most jobs become a status quo. You have a role, you fulfill it. If you excel, there is the potential for promotion. But if you work on a contract for a service company, promotions and pay increases are impacted by the terms of the contract. Usually your company can't simply pay you more and charge the customer more to cover it. Usually they can't create a new positio
Joining a company should be about opportunity. Personal, professional, and fiscal. But where does that opportunity come from? Most jobs become a status quo. You have a role, you fulfill it. If you excel, there is the potential for promotion. But if you work on a contract for a service company, promotions and pay increases are impacted by the terms of the contract. Usually your company can't simply pay you more and charge the customer more to cover it. Usually they can't create a new positio- 0 comments
- 6,271 views
-
 Great proposal writing isn't based on slick words. Great proposal writing does not require the editing skills of a professional. You really don’t have to be an expert in anything to be a great proposal writer. But there is one thing that is absolutely necessary, and not everyone has it. I’m not even sure that everyone can develop it. That thing is perspective. To write a great proposal, you must be able to conceive which words to use from the customer’s perspective. You must be able to thi
Great proposal writing isn't based on slick words. Great proposal writing does not require the editing skills of a professional. You really don’t have to be an expert in anything to be a great proposal writer. But there is one thing that is absolutely necessary, and not everyone has it. I’m not even sure that everyone can develop it. That thing is perspective. To write a great proposal, you must be able to conceive which words to use from the customer’s perspective. You must be able to thi- 0 comments
- 19,662 views
-
 Subject matter experts or project managers often write the technical approach in response to the statement of work in a proposal. The Technical Approach volume addresses what you propose to do or deliver to the customer. Writing the technical approach often requires significant technical subject matter expertise. What the subject matter experts may lack in writing and fine art skills, they often make up for with enthusiasm for their subject. When they bring that enthusiasm to the proposal,
Subject matter experts or project managers often write the technical approach in response to the statement of work in a proposal. The Technical Approach volume addresses what you propose to do or deliver to the customer. Writing the technical approach often requires significant technical subject matter expertise. What the subject matter experts may lack in writing and fine art skills, they often make up for with enthusiasm for their subject. When they bring that enthusiasm to the proposal,- 0 comments
- 73,291 views
-
 Bid decisions are all about ROI. And your ROI is directly impacted by your win rate. Low win rates lead to a low ROI. High win rates make it all worthwhile. For some companies, a 10% increase in win rate is the same as a 40% increase in leads pursued. Bad bid decisions lead to a lower win rate. Bid decisions have a major impact on your ROI. If you care about ROI, then even though it's counter intuitive, you do not want to bid every opportunity you encounter. This isn’t about subjective pref
Bid decisions are all about ROI. And your ROI is directly impacted by your win rate. Low win rates lead to a low ROI. High win rates make it all worthwhile. For some companies, a 10% increase in win rate is the same as a 40% increase in leads pursued. Bad bid decisions lead to a lower win rate. Bid decisions have a major impact on your ROI. If you care about ROI, then even though it's counter intuitive, you do not want to bid every opportunity you encounter. This isn’t about subjective pref- 0 comments
- 7,988 views
-
 Maximizing win probability requires going beyond simply trying to provide the best response to the customer’s requirements. This is because: The customer is more than one person. Evaluators often have different ideas about which submission is “best.” We often do not know who will be participating in the evaluation. And yet, we know we need to write our proposals from the customer’s perspective instead of our own. This makes understanding the range of perspectives th
Maximizing win probability requires going beyond simply trying to provide the best response to the customer’s requirements. This is because: The customer is more than one person. Evaluators often have different ideas about which submission is “best.” We often do not know who will be participating in the evaluation. And yet, we know we need to write our proposals from the customer’s perspective instead of our own. This makes understanding the range of perspectives th- 0 comments
- 1,308 views
-
 There are some words you should avoid in your proposals, but most of them simply relate to unsubstantiated claims. A list of words that you should use in your proposals is a lot harder because every customer is different. If you focus on the words that should go in your proposal, you might overlook the power of a word that might not actually appear in the proposal, but that can make all the difference regarding what you do put into it. Most people only think about “what” should go in their
There are some words you should avoid in your proposals, but most of them simply relate to unsubstantiated claims. A list of words that you should use in your proposals is a lot harder because every customer is different. If you focus on the words that should go in your proposal, you might overlook the power of a word that might not actually appear in the proposal, but that can make all the difference regarding what you do put into it. Most people only think about “what” should go in their- 0 comments
- 9,101 views
-
 When you get lucky and your customer reveals something they’re thinking about doing or buying in the future, your next step should not be to pitch them on selecting you as the vendor. Instead, what you should focus on next is: Gaining an information advantage Influencing the specification Building the relationship so that more revelations may follow Besides, any deal is weeks or months away. Maybe even years. And more importantly, the customer isn't ready to think about
When you get lucky and your customer reveals something they’re thinking about doing or buying in the future, your next step should not be to pitch them on selecting you as the vendor. Instead, what you should focus on next is: Gaining an information advantage Influencing the specification Building the relationship so that more revelations may follow Besides, any deal is weeks or months away. Maybe even years. And more importantly, the customer isn't ready to think about- 0 comments
- 3,561 views
-
 Proposal losses generally fall into these categories: Price Your proposal didn't score high enough against the evaluation criteria Someone had an offering that the customer liked better You made mistakes or didn’t follow the instructions Presentation So when a proposal loses, why do people tend to focus the lessons learned on how the proposal was written? The truth is that you probably lost before the proposal started.
Proposal losses generally fall into these categories: Price Your proposal didn't score high enough against the evaluation criteria Someone had an offering that the customer liked better You made mistakes or didn’t follow the instructions Presentation So when a proposal loses, why do people tend to focus the lessons learned on how the proposal was written? The truth is that you probably lost before the proposal started.- 0 comments
- 3,527 views
-
 An Executive Summary for a proposal is not really a summary at all. If you are the customer receiving a proposal, do you really want to read a redundant summary before reading the proposal? Or do you want to find out what you’re going to get if you accept the proposal? An Executive Summary is a tool to help the reader make their decision and the evaluator to score the proposal. Extra and unnecessary reading that gets in the way and tends to annoy customers. Writing an Executive Summary that is r
An Executive Summary for a proposal is not really a summary at all. If you are the customer receiving a proposal, do you really want to read a redundant summary before reading the proposal? Or do you want to find out what you’re going to get if you accept the proposal? An Executive Summary is a tool to help the reader make their decision and the evaluator to score the proposal. Extra and unnecessary reading that gets in the way and tends to annoy customers. Writing an Executive Summary that is r- 0 comments
- 7,939 views
-
 Is proposal layout design just the icing on the cake? Does it improve your chances of winning? Is presentation everything? Or is it completely irrelevant to the decision maker? How much do impressions matter? How much effort should you put into the design of your proposal layout? What is the most important priority? I think it is like Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs applied to proposals. At the base, and your first priority, is RFP compliance. If you are not compliant with the requiremen
Is proposal layout design just the icing on the cake? Does it improve your chances of winning? Is presentation everything? Or is it completely irrelevant to the decision maker? How much do impressions matter? How much effort should you put into the design of your proposal layout? What is the most important priority? I think it is like Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs applied to proposals. At the base, and your first priority, is RFP compliance. If you are not compliant with the requiremen- 0 comments
- 11,962 views
-
 In order to win in writing, it’s crucial to be able to read your proposal the same way your customer reads it. The customer doesn’t read a proposal like a book. They probably won't even read parts of it at all! Customers read proposals with one or more purposes or goals in mind. The customer might score your proposal, compare it, or look for answers to the questions they have. What you put into your proposal should not be based on what you want to say. It should be based on what your custom
In order to win in writing, it’s crucial to be able to read your proposal the same way your customer reads it. The customer doesn’t read a proposal like a book. They probably won't even read parts of it at all! Customers read proposals with one or more purposes or goals in mind. The customer might score your proposal, compare it, or look for answers to the questions they have. What you put into your proposal should not be based on what you want to say. It should be based on what your custom- 0 comments
- 17,564 views
-
 Sometimes it helps more to know what not to do than it helps to hear more about “best practices” and all the things you should be doing. You can use this like a checklist to see where you might have gone wrong and improve your Executive Summary writing: Start your Executive Summary by introducing yourself. From the customer’s perspective, you are not as important as what they are going to get if they accept your proposal. Summarizing your qualifications. Whether or not you are qua
Sometimes it helps more to know what not to do than it helps to hear more about “best practices” and all the things you should be doing. You can use this like a checklist to see where you might have gone wrong and improve your Executive Summary writing: Start your Executive Summary by introducing yourself. From the customer’s perspective, you are not as important as what they are going to get if they accept your proposal. Summarizing your qualifications. Whether or not you are qua- 0 comments
- 9,473 views
-
 Congratulations! Either you got promoted or have started your own company. You’re an executive with profit and loss responsibility now, and must grow your business. You probably have some experience with business development, sales, or proposals, but being in charge of it is another matter. That’s okay, because like most executives, you’re confident you can make the stretch. My goal in writing this is to help you avoid falling into traps that look rational, but will weaken your competitiven
Congratulations! Either you got promoted or have started your own company. You’re an executive with profit and loss responsibility now, and must grow your business. You probably have some experience with business development, sales, or proposals, but being in charge of it is another matter. That’s okay, because like most executives, you’re confident you can make the stretch. My goal in writing this is to help you avoid falling into traps that look rational, but will weaken your competitiven- 0 comments
- 6,593 views
-
 At most companies, the proposal management role is not well defined. What you are managing is not well defined. The processes you are supposed to implement are neither written nor well defined. Who you are managing is not well defined. The resources at your disposal are not well defined, and they're usually minimal. Your responsibilities are all-encompassing. In larger companies, there are multiple roles (business development, capture, subject matter experts, writers, proposal specialists,
At most companies, the proposal management role is not well defined. What you are managing is not well defined. The processes you are supposed to implement are neither written nor well defined. Who you are managing is not well defined. The resources at your disposal are not well defined, and they're usually minimal. Your responsibilities are all-encompassing. In larger companies, there are multiple roles (business development, capture, subject matter experts, writers, proposal specialists,- 0 comments
- 10,365 views
-
 Effective proposal management requires thorough expectation management. But while some expectations will be the same for every proposal, many will change. Many will need to be determined, figured out, or updated as things change during the proposal. But with a little structure, you can improve how you communicate expectations and do a better job of making sure everything is covered. Remember: If you overwhelm people with too much information about expectations, they will not absorb it
Effective proposal management requires thorough expectation management. But while some expectations will be the same for every proposal, many will change. Many will need to be determined, figured out, or updated as things change during the proposal. But with a little structure, you can improve how you communicate expectations and do a better job of making sure everything is covered. Remember: If you overwhelm people with too much information about expectations, they will not absorb it- 0 comments
- 1,436 views

